---
title: oopcpp实践2025-2026-1全作业
---
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
## 作业
### 1. ClassDraw
#### 题目

#### 参考答案
```cpp title="Draw.h"
#pragma once
/*
* @Description: 绘制类
*/
class Draw
{
public:
Draw(char what, int down, int across);
void DrawWall();
void DrawBox();
void DrawTriangle();
private:
char what;
int down;
int across;
};
```
```cpp title="Draw.cpp"
#include "Draw.h"
#include
#include
/*
* @Description: 绘制类的构造函数
* @param {char} what 绘制的字符
* @param {int} down 绘制的行数
* @param {int} across 绘制的列数
*/
Draw::Draw(char what, int down, int across) {
assert(down >= 0 && across >= 0 && "down or across should >= 0 !"); // 断言,确保 down 和 across 大于等于 0
this->what = what;
this->down = down;
this->across = across;
}
/*
* @Description: 绘制墙
*/
void Draw::DrawWall() {
for (int i = 0; i < this->down; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < this->across; j++) {
std::cout << this->what;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
/*
* @Description: 绘制盒子
*/
void Draw::DrawBox() {
for (int i = 0; i < this->down; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < this->across; j++) {
if (i != 0 && i != down - 1 && j != 0 && j != across - 1) {
std::cout << " ";
}
else {
std::cout << this->what;
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
/*
* @Description: 绘制三角形
*/
void Draw::DrawTriangle() {
int h = down > across ? down : across;
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i+1; j++) {
std::cout << this->what;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
```
```cpp title="main.cpp"
// file encode: UTF-8
#include "Draw.h"
#include
#include
const std::set TYPES = { -1,1,2,3 }; // 合法的绘制类型
/*
* @Description: 主函数
*/
int main()
{
char what = ' ';
int across = 0, down = 0, type = 0;
while (true) {
std::cout << "Please input the shape you want to draw: 1-wall, 2-box, 3-triangle, -1 for end" << std::endl;
std::cin >> type;
if (TYPES.count(type)) {
if (type == -1) {
return 0;
}
else {
std::cout << "input the letter to fill the shape" << std::endl;
std::cin >> what;
std::cout << "height" << std::endl;
std::cin >> down;
std::cout << "width" << std::endl;
std::cin >> across;
if (down < 0 || across < 0) {
std::cout << "height and width should bigger than 0" << std::endl;
continue;
}
Draw draw(what, down, across);
switch (type) {
case 1:
draw.DrawWall();
break;
case 2:
draw.DrawBox();
break;
case 3:
draw.DrawTriangle();
break;
}
}
}
else {
std::cout << "illegal input, please input again!" << std::endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
```
### 2. ClassDecrypt
#### 题目
#### 参考答案
```cpp title="main.cpp"
#include
#include
class Decrypt {
std::string s;
int key;
public:
Decrypt();
Decrypt(std::string s,int key);
int GetKey();
void PrintKey();
void GetString();
void Print();
void PrintAnswer();
};
Decrypt::Decrypt() { // 默认初始化
this->s="hello,world!";
this->key=1;
}
Decrypt::Decrypt(std::string s,int key) { // 按照给定的s与key初始化
this->s=s;
this->key=key;
}
int Decrypt::GetKey() { // 获取key值
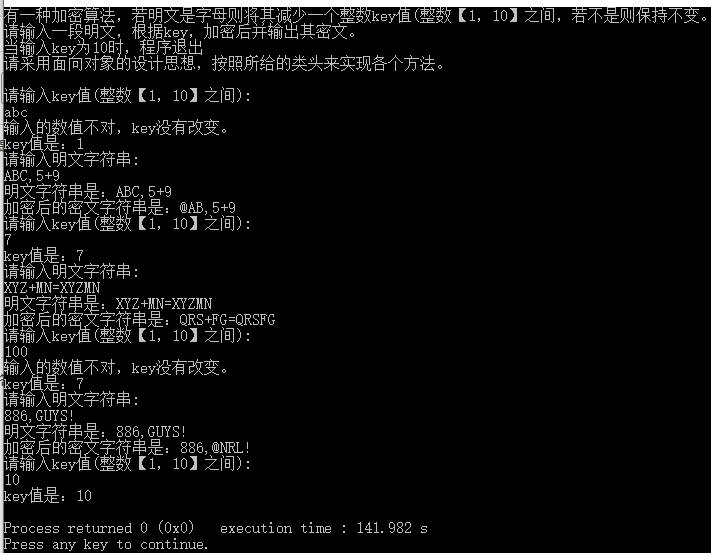
std::cout << "请输入key值(整数【1,10】之间):\n";
std::string num; // 采用string读入提高代码健壮性
getline(std::cin,num); // 使用getline避免本行输入中出现空格污染后续输入
if(num == "10") { // 特殊判断输入为10的情况
this -> key = 10;
return this -> key;
}
else if(num.size() == 1 && num[0]>='1' && num[0] <= '9') { // 如果输入合法,改变key值
this->key = num[0] - '0';
return this->key;
}
else { // 输入非法,输出提示
std::cout << "输入的数值不对,key没有改变。\n";
return 0;
}
}
void Decrypt::PrintKey() { // 输出当前key值
std::cout << "key值是:" << this -> key << '\n';
if(this -> key == 10) { // 如果key在上一步被更改为10,终止程序
exit(0);
}
return;
}
void Decrypt::GetString() { // 获取明文字符串
std::cout << "请输入明文字符串:\n";
std::string str;
getline(std::cin,str); // 采用getline防止无法读入明文字符串中潜在的空格
this->s=str;
return ;
}
void Decrypt::Print() { // 输出明文字符串
std::cout << "明文字符串是:";
std::cout << this->s << '\n';
return ;
}
void Decrypt::PrintAnswer() { // 加密字符串
for(int i = 0; i < this->s.size(); i++) { // 加密并修改字符串
if(this->s[i] >= 'a' && this->s[i] <= 'z') {
this->s[i] -= key;
}
else if(this->s[i] >= 'A' && this->s[i] <= 'Z') {
this->s[i] -= key;
}
}
std::cout << "加密后的密文字符串是:" << this -> s << '\n'; // 在此处输出加密字符串
return ;
}
int main() {
Decrypt test;
while(true) { // 循环在PrintKey()函数中key==10的情况下终止
test.GetKey();
test.PrintKey();
test.GetString();
test.Print();
test.PrintAnswer();
}
return 0;
}
```
> 教师批语:
>
> 程序的退出逻辑被放在了 PrintKey函数中,很怪。
> 一个更合理的做法是在 main函数的循环中检查 GetKey的返回值,并决定是否退出。
### 3. ClassRandom
#### 题目
#### 参考答案
```cpp title="main.cpp"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
class Random
{
public:
int type,left, right, adv; //从左至右分别为 操作类型、最小值、最大值、均值
Random(bool pseudo);
int reseed();
double random_real();
int poisson(double mean);
int input_positive_int();
double input_positive_double();
std::vector rand6();
private:
int seed, multiplier, add_on;
};
Random::Random(bool pseudo) // 构造函数
{
if (pseudo)
seed = 1;
else
seed = time(NULL) % INT_MAX;
multiplier = 2743;
add_on = 5923;
type = 0;
}
int Random::reseed() // 种子生长函数
{
seed = seed * multiplier + add_on;
return seed;
}
double Random::random_real()
{
double max = INT_MAX + 1.0; // INT_MAX = (2)31 -1
double temp = reseed();
if (temp < 0)
temp = temp + max;
return temp / max;
}
int Random::poisson(double mean)
{
double limit = exp(-mean);
double product = random_real();
int count = 0;
while (product > limit)
{
count++;
product *= random_real();
}
return count;
}
int Random::input_positive_int() // 以字符串形式读入一个正整数
{
std::string str;
std::cin >> str;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
if (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9')
{
res *= 10;
res += str[i] - '0';
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
if(res <= 0) res = -1;
return res;
}
double Random::input_positive_double() // 以字符串形式读入一个小数
{
std::string str;
std::cin >> str;
double res = 0, now = 1;
bool dot = false;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
if (str[i] == '.') // 判断小数点是否出现过
{
if (dot)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
dot = true;
}
}
else if (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9')
{
if(dot) // 处理小数部分
{
now /= 10;
res += (str[i] - '0') * now;
}
else // 处理整数部分
{
res *= 10;
res += str[i] - '0';
}
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
if(res <= 0) res = -1;
return res;
}
std::vector Random::rand6() // 生成六个范围内的随机数
{
std::vector res(6);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
res[i] = random_real() * (right - left) + left;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
Random r(false);
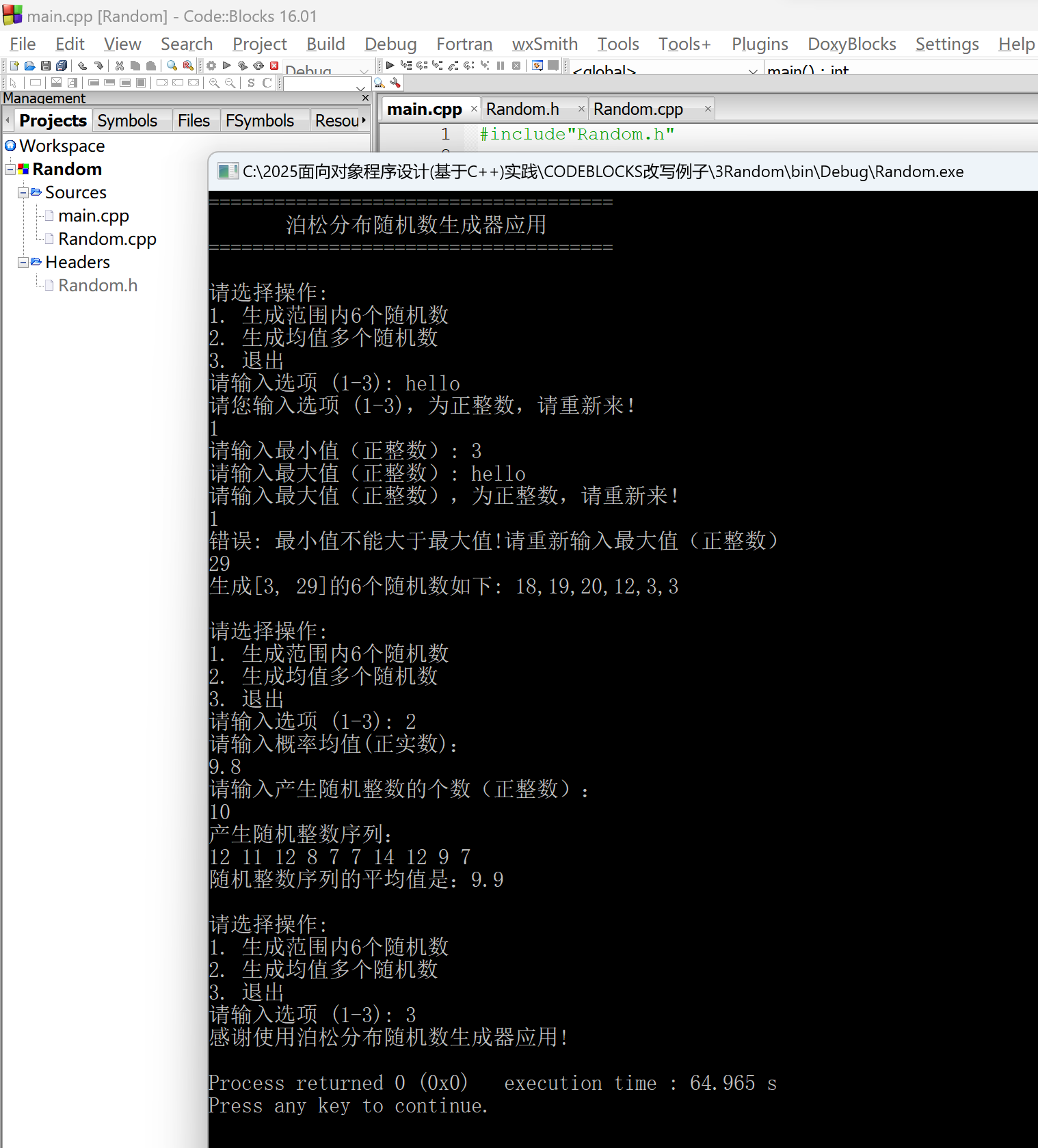
std::cout << "=====================================\n";
std::cout << " 泊松分布随机数生成器应用 \n";
std::cout << "=====================================\n";
while (r.type != 3)
{
std::cout << "\n";
std::cout << "请选择操作:\n";
std::cout << "1. 生成范围内6个随机数\n";
std::cout << "2. 生成均值多个随机数\n";
std::cout << "3. 退出\n";
std::cout << "请输入选项(1-3):";
r.type = r.input_positive_int();
while (r.type < 1 || r.type > 3) // 确保输入类型符合预期
{ // 我承认这么写看起来很丑
std::cout << "请您输入选项(1-3),为正整数,请重新来!\n"; // 但我一时想不到相对更好的写法
r.type = r.input_positive_int();
}
if (r.type == 1) // 生成区间内六个随机数
{
std::cout << "请输入最小值(正整数):";
r.left = r.input_positive_int();
while (r.left < 1)
{
std::cout << "请输入最小值(正整数),为正整数,请重新来!\n";
r.left = r.input_positive_int();
}
std::cout << "请输入最大值(正整数):";
r.right = r.input_positive_int();
while (r.right < 1 || r.right < r.left)
{
if (r.right < 1)
std::cout << "请输入最大值(正整数),为正整数,请重新来!\n";
else if (r.right < r.left)
std::cout << "错误:最小值不能大于最大值!请重新输入最大值(正整数)\n";
r.right = r.input_positive_int();
}
std::vector res = r.rand6();
std::cout << "生成[" << r.left << "," << r.right << "]的6个随机数如下:";
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
std::cout << res[i] << (i < 5 ? ", " : "\n");
}
}
else if (r.type == 2) // 生成给定均值的泊松分布随机数
{
std::cout << "请输入概率均值(正实数):\n";
r.adv = r.input_positive_double();
while (r.adv <= 0)
{
std::cout << "请您概率均值(正实数),为正实数,请重新来!\n"; // 此处拼写错误系给定示例程序原文,故原文保留
r.adv = r.input_positive_double();
}
int num;
std::cout << "请输入产生随机整数的个数(正整数):\n";
num = r.input_positive_int();
while (num < 1) {
std::cout << "请您请输入产生随机整数的个数(正整数),为正整数,请重新来!\n";
num = r.input_positive_int();
}
long long sum = 0; // 计算随机整数之和
std::cout << "产生随机整数序列:\n";
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
int res = r.poisson(r.adv);
sum += res;
std::cout << res << ' ';
}
// 示例程序计算均值似乎有误,已修复此问题
std::cout << "\n随机整数序列的平均值是:" << (double)sum/num << '\n';
}
}
std::cout << "感谢使用泊松分布随机数生成器应用!\n";
return 0;
}
```
> 教师批语:
>
> rand6 函数中,
> 生成随机数的公式为 random_real() * (right - left) + left,
> 这样生成的随机数范围实际上是 [left, right),永远无法生成最大值 right
### 4. ClassTime
#### 题目
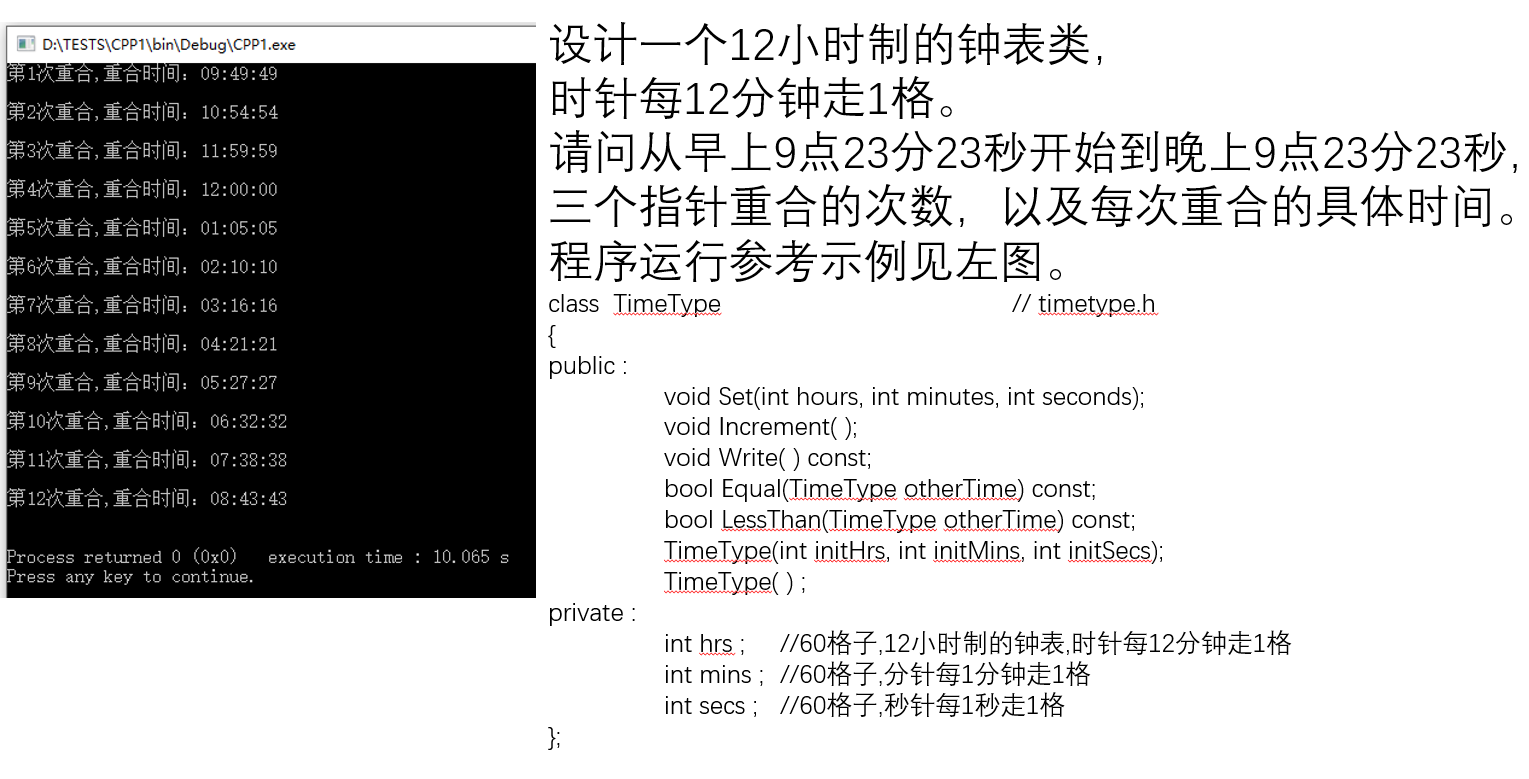

#### 参考答案
```cpp title="main.cpp"
#include
#include
#include
class TimeType
{
public:
void Set(int hours, int minutes, int seconds);
void Increment();
void Write() const;
bool Equal(TimeType otherTime) const;
bool Lessthan(TimeType otherTime) const;
TimeType(int initHrs, int initMins, int initSecs);
TimeType();
bool Overlap();
private:
int hrs;
int mins;
int secs;
};
void TimeType::Set(int hours, int minutes, int seconds) // 将函数参数赋给类中的变量
{
this->hrs = hours;
this->mins = minutes;
this->secs = seconds;
return;
}
void TimeType::Increment() // 让类增加一秒
{
this->secs++;
if (this->secs == 60) // 处理 60 秒 -> 1 分钟进位
{
this->secs = 0;
this->mins++;
}
if (this->mins == 60) // 处理 60 分钟 -> 1 小时进位
{
this->mins = 0;
this->hrs++;
}
if (this->hrs == 24) // 处理 24 小时 -> 1 天进位
{
this->hrs = 0;
}
return;
}
void TimeType::Write() const
{
if (this->hrs == 12 || this->hrs == 0) // 特殊处理 0 点和 12 点
printf("12");
else //输出当前小时
printf("%02d", this->hrs%12);
printf(":%02d:%02d\n", this->mins, this->secs); // 以保留两位有效数字形式输出当前分钟与秒
return;
}
bool TimeType::Equal(TimeType otherTime) const // 当且仅当小时,分钟,秒三个变量均相等的时候返回 True
{
return this->hrs == otherTime.hrs &&
this->mins == otherTime.mins &&
this->secs == otherTime.secs;
}
bool TimeType::Lessthan(TimeType otherTime) const // 将类中时间转换为自00:00:00过去了多少秒,然后比较大小,只能比较同一天内的时间
{
return (this->hrs * 3600 + this->mins * 60 + this->secs) < (otherTime.hrs * 3600 + otherTime.mins * 60 + otherTime.secs);
}
TimeType::TimeType(int initHrs, int initMins, int initSecs) // 构造函数
{
this->hrs = initHrs;
this->mins = initMins;
this->secs = initSecs;
}
TimeType::TimeType() // 构造函数
{
this->hrs = 0;
this->mins = 0;
this->secs = 0;
}
bool TimeType::Overlap() // 判断三个指针是否重合
{
return this->mins == this->secs && this->mins / 12 + this->hrs % 12 * 5 == this->mins;
}
int main()
{
TimeType beg(9, 23, 23), end(21, 23, 23);
int num = 0;
for (TimeType i = beg; !i.Equal(end); i.Increment()) // 考虑到可能需要更换参数处理跨天的情况,故采用了 !!i.Equal(end) 而非 i.Increment() 作为循环条件
{
if (i.Overlap())
{
std::string s; // 作为吞掉输入的临时变量,无实际意义
num++; // 计算当前是第多少次重合
std::cout << "-------------------------------------\n"; //参考示例程序,输出上分割线
std::cout << "第" << num << "次重合,重合时间:";
i.Write();
std::cout << "-------------------------------------\n";
std::getline(std::cin, s); // 根据实际测试,示例程序应该是采用的getchar(),但是出于美观性的考虑,本处采用了getline()
}
}
return 0;
}
```
### 5. CBrowser
#### 题目
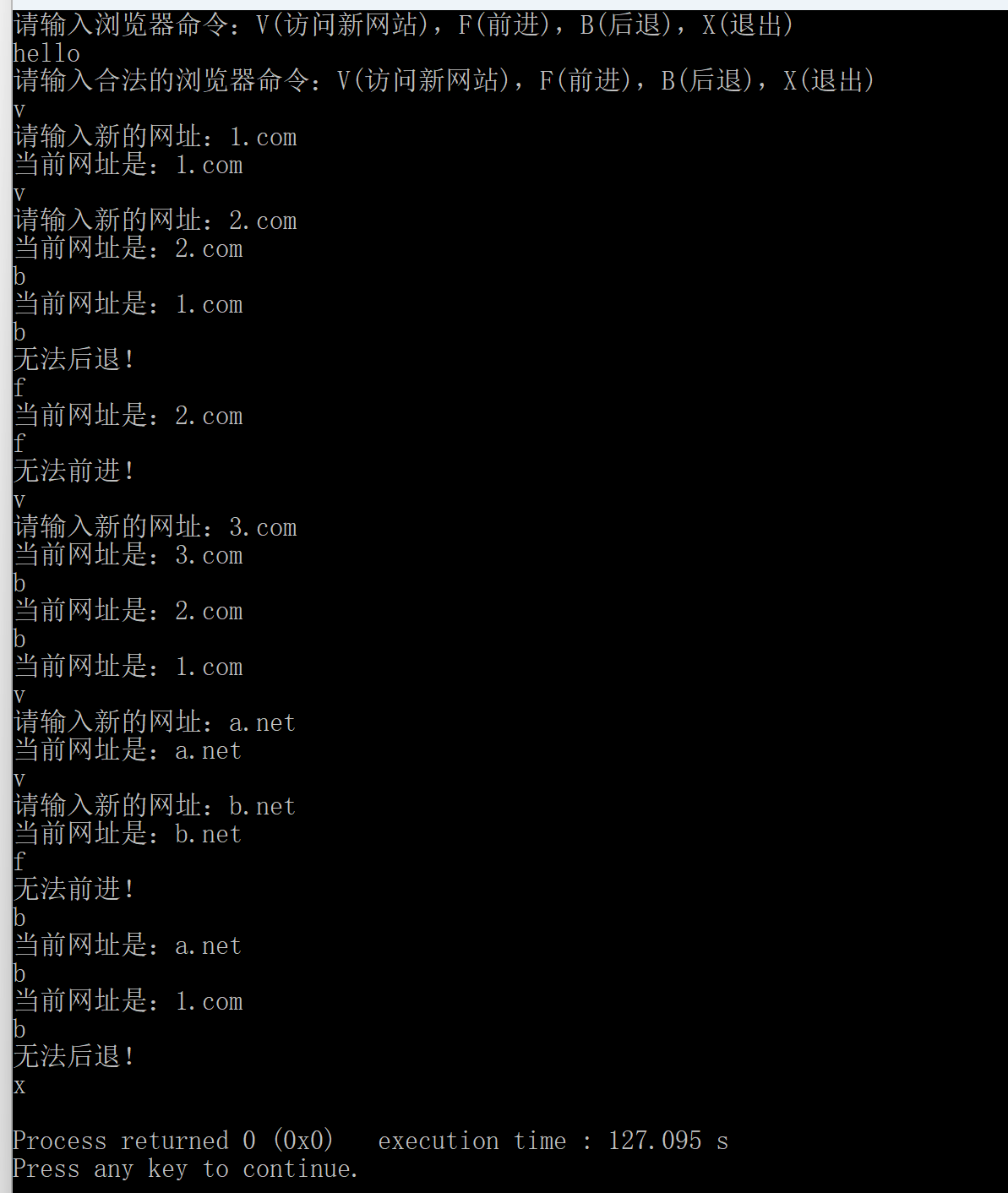
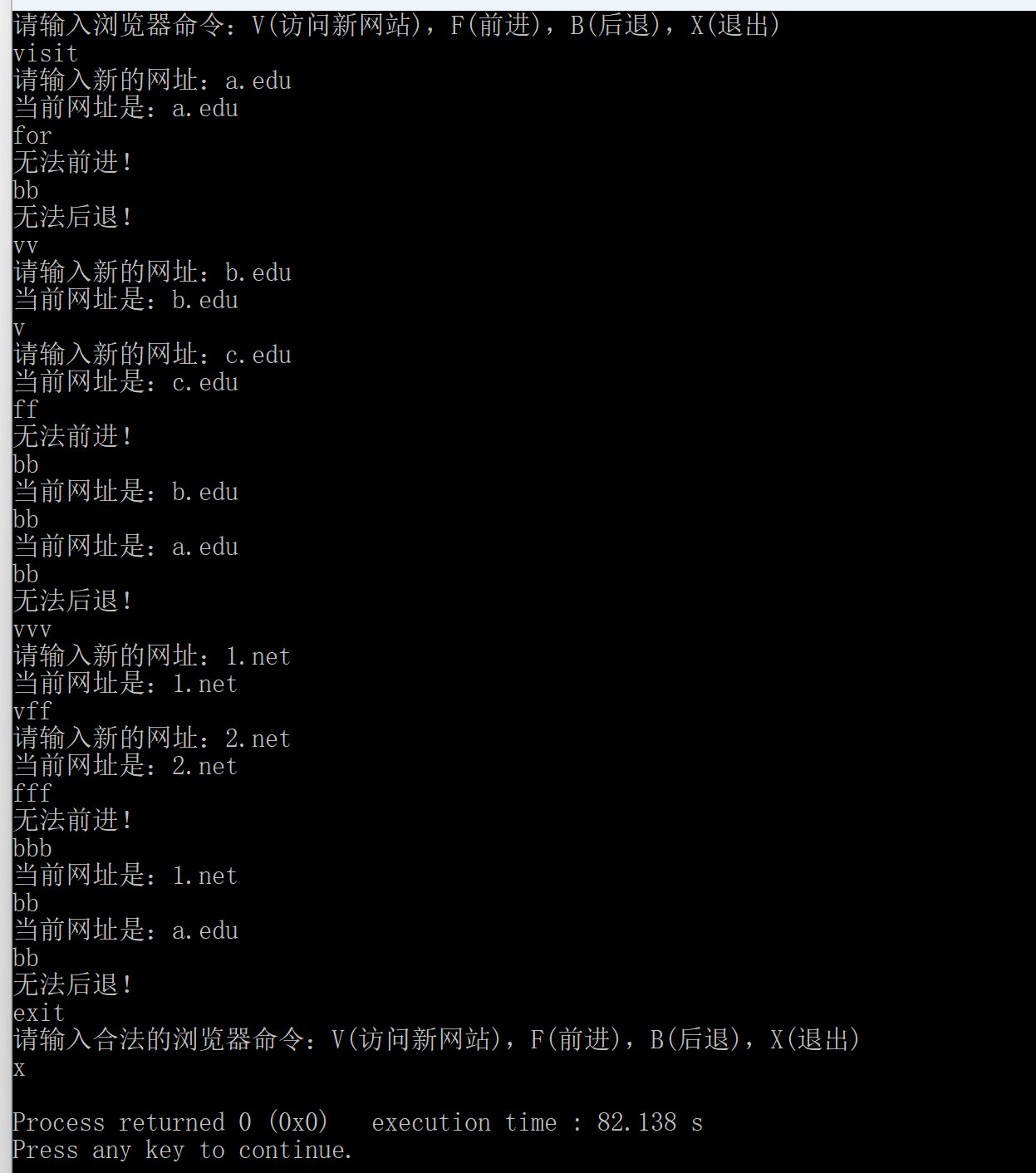
#### 参考答案
```cpp title="brouser.h"
template
struct Node
{
// data members
Node_entry entry;
Node *next;
Node *back;
// constructors
Node();
Node(Node_entry item, Node *link_back = 0, Node *link_next = 0);
~Node();
};
template
class CBrowser
{
private:
// data members
Node *current; // 当前游标指针
public:
// constructors
bool CanForward(); // 可以继续往前
bool Forward(); // 前进一个节点
bool CanBack(); // 可以继续后退
bool Back(); // 后退一个节点
void NewSite(Node_entry site); // 将新的site插入到current当前位置的后面
Node *GetCurrent(); // 获得当前游标指针current
CBrowser(); // 缺省构造,空链表
~CBrowser(); // 析构,释放所有节点内存
};
template
Node::Node()
{
this->entry = "";
this->back = nullptr;
this->next = nullptr;
}
template
Node::Node(Node_entry item, Node *link_back, Node *link_next)
{
this->entry = item;
this->back = link_back;
this->next = link_next;
}
template // 递归删除此节点及其所有后继节点
Node::~Node()
{
if (this->next != nullptr)
{
delete this->next;
}
}
template // 检测当前节点的next指针是否为空以判断是否存在后继节点
bool CBrowser::CanForward()
{
return (this->current->next != nullptr);
}
template
bool CBrowser::Forward()
{
if (this->CanForward())
{
this->current = this->current->next;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
template // 采用了含头节点的双向链表
bool CBrowser::CanBack() // 故检测当前节点的back指针的back指针是否为空检测该节点前驱节点是否为头节点
{ // 等价于检测该节点是否存在前驱节点
return (this->current->back->back != nullptr);
}
template
bool CBrowser::Back()
{
if (this->CanBack())
{
this->current = this->current->back;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
template
void CBrowser::NewSite(Node_entry site)
{
delete this->current->next; // 先删除当前节点的所有后继节点
Node *newSite = new Node(site, this->current, nullptr);
newSite->entry = site; // 然后使当前节点的后继节点为新节点
this->current->next = newSite; // 设定指针
this->current = newSite; // 将当前节点转移至后继节点
}
template
Node *CBrowser::GetCurrent()
{
return this->current;
}
template
CBrowser::CBrowser()
{
current = new Node;
}
template
CBrowser::~CBrowser()
{
delete this->current;
}
```
```cpp title="main.cpp"
#include
#include
#include "brouser.h"
int main()
{
std::cout << "请输入浏览器命令:V(访问新网站),F(前进),B(后退),X(退出)\n";
CBrowser log; // 创建浏览器历史记录链表
char command = 0; // 存储当前指令
while (command != 'X')
{
std::string input;
getline(std::cin, input); // 使用getline()读取字符串作为指令
command = input.front(); // 取字符串首字符做指令模糊匹配
if (command >= 'a' && command <= 'z') // 处理大小写敏感
{
command -= 'a';
command += 'A';
}
std::string website;
switch (command)
{
case 'V':
std::cout << "请输入新的网址:";
getline(std::cin, website); // 使用getline()读入新网址
log.NewSite(website);
std::cout << "当前网址是:" << log.GetCurrent()->entry << '\n';
break;
case 'F':
if (log.Forward())
{
std::cout << "当前网址是:" << log.GetCurrent()->entry << '\n';
}
else
{
std::cout << "无法前进!\n";
}
break;
case 'B':
if (log.Back())
{
std::cout << "当前网址是:" << log.GetCurrent()->entry << '\n';
}
else
{
std::cout << "无法后退!\n";
}
break;
case 'X':
break;
default:
std::cout << "请输入合法的浏览器命令:V(访问新网站),F(前进),B(后退),X(退出)\n"; // 处理读入非法命令的情况
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
```
### 6. CTypes
#### 题目
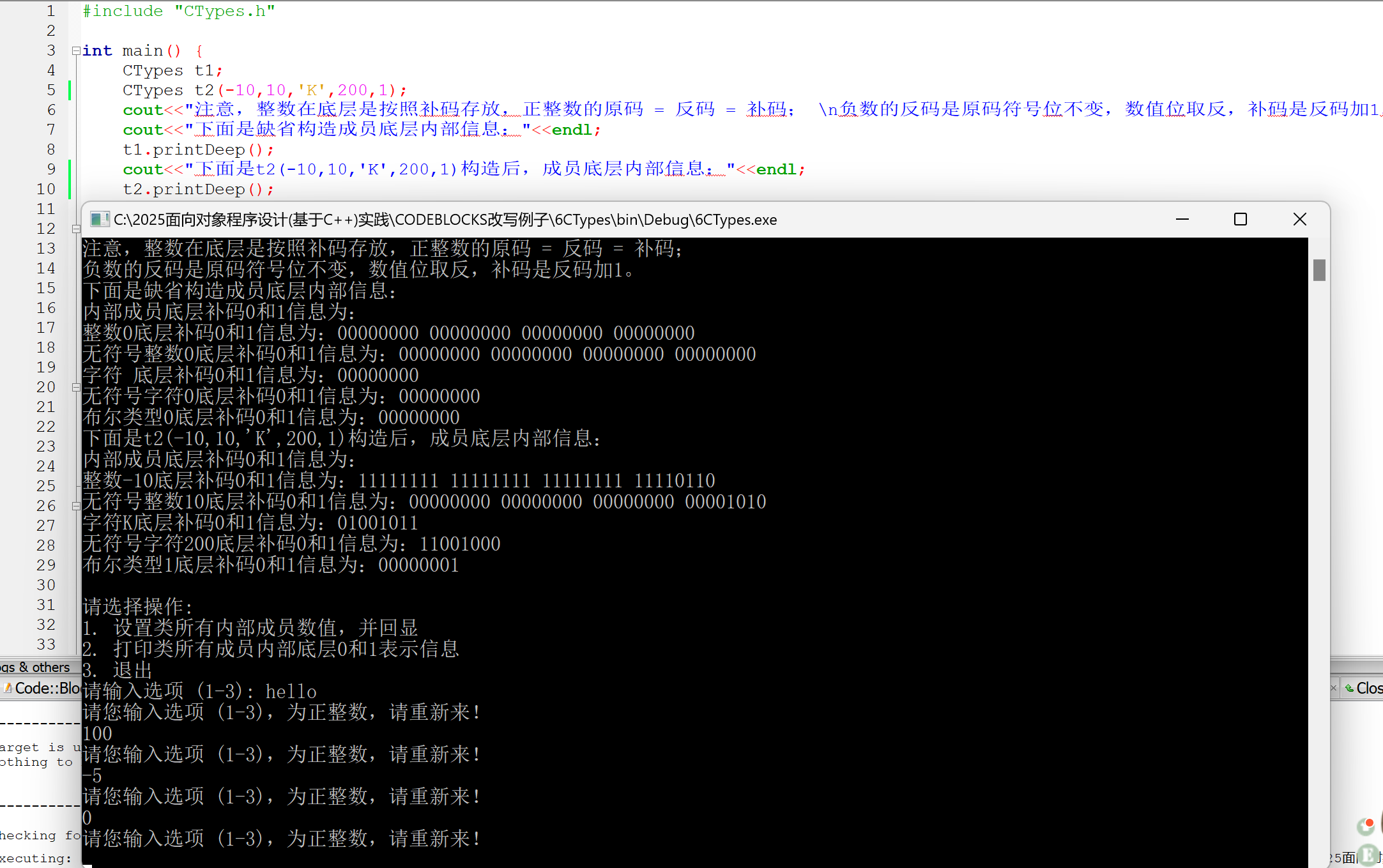
#### 参考答案
```cpp title="main.cpp"
#include
using namespace std;
long long input_int(string str) // 以字符串形式读入一个正整数,从之前写的随机数类作业中拿过来的
{
long long res = 0;
long long i = 0;
bool negative = false;
if (str.front() == '-') // 处理负号
{
negative = true;
i++;
}
for (; i < str.size(); i++)
{
if (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9')
{
res *= 10;
res += str[i] - '0';
}
else //非法值一律返回0,在函数内再进行判断
{
return 0;
}
}
return negative ? -res : res;
}
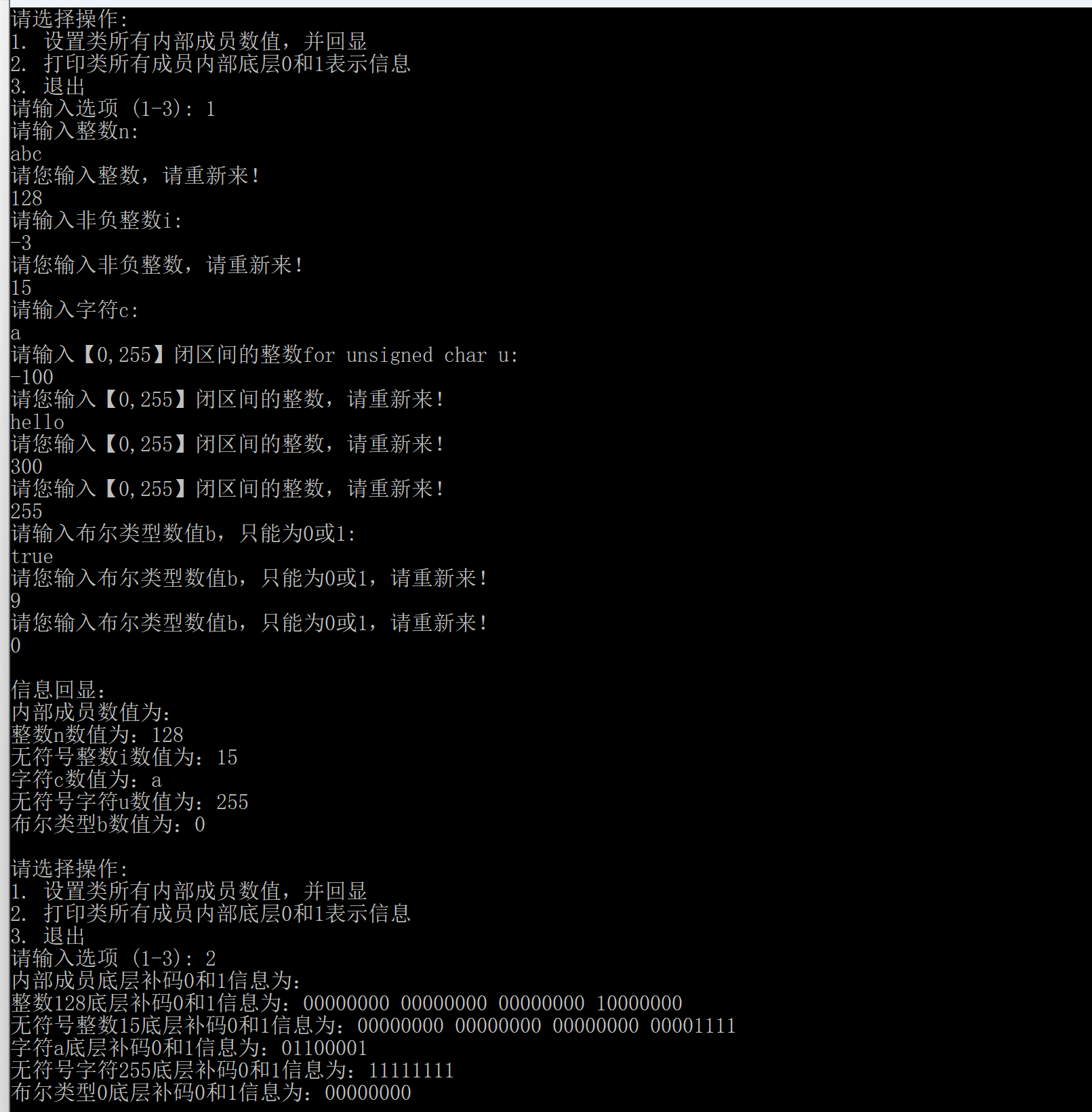
class CTypes
{
public:
CTypes(); // 缺省构造函数,所有成员初始化为0
CTypes(int n, unsigned int i, char c, unsigned char u, bool b); // 构造函数,所有成员初始化为形参
void setValue(); // 设置内部成员数据数值
void printValue(); // 输出内部成员数据数值
void printDeep(); // 输出所有内部成员数据底层补码的存放信息
private:
void printBinary(void *var, size_t size); // 打印指针var指向任意变量(字节数为size)的底层二进制表示
// size_t 是一个无符号整数类型,32位系统unsigned int(4字节)64位系统unsigned long(8字节)
// void * 是一种特殊的指针类型,称为 "无类型指针" 或 "泛型指针",在解引用,或者+-操作之前,必须将其转换为具体的指针类型。
// 内部成员:
int n;
unsigned int i;
char c;
unsigned char u;
bool b;
};
CTypes::CTypes() //缺省构造
{
this->n = 0;
this->i = 0;
this->c = '\0';
this->u = '\0';
this->b = false;
}
CTypes::CTypes(int n, unsigned int i, char c, unsigned char u, bool b) //给定值构造
{
this->n = n;
this->i = i;
this->c = c;
this->u = u;
this->b = b;
}
void CTypes::setValue()
{
string str;
long long temp;
cout << "请输入整数n:\n";
while (1)
{
getline(cin, str);
temp = input_int(str);
if (temp == 0 && str != "0") //此处判断返回值为0是读入了非法值还是读入了0
{
cout << "请您输入整数,请重新来!\n";
}
else
{
this->n = temp;
break;
}
}
cout << "请输入非负整数i:\n";
while (1)
{
getline(cin, str);
temp = input_int(str);
if (temp == 0 && str != "0")
{
cout << "请您输入非负整数,请重新来!\n";
}
else if (temp < 0) //返回负数的时候同样作为非法值处理
{
cout << "请您输入非负整数,请重新来!\n";
}
else
{
this->i = temp;
break;
}
}
cout << "请输入字符c:\n"; // 按照样例程序,此处输入字符串时保留第一个字符
getline(cin, str);
this->c = str.front();
cout << "请输入【0,255】闭区间的整数for unsigned char u:\n";
while (1)
{
getline(cin, str);
temp = input_int(str);
if (temp == 0 && str != "0")
{
cout << "请您输入【0,255】闭区间的整数,请重新来!\n";
}
else if (temp < 0 || temp > 255) //处理返回范围外的非法值
{
cout << "请您输入【0,255】闭区间的整数,请重新来!\n";
}
else
{
this->u = temp;
break;
}
}
cout << "请输入布尔类型数值b,只能为0或1:\n";
while (1) //因为布尔类型情形简单,只需要判断两种情况,便不调用字符串转整数函数了
{
getline(cin, str);
if (str == "0")
{
this->b = false;
break;
}
else if (str == "1")
{
this->b = true;
break;
}
else
{
cout << "请您输入布尔类型数值b,只能为0或1,请重新来!\n";
}
}
return;
}
void CTypes::printValue() //打印变量
{
cout << "内部成员数值为:" << endl;
cout << "整数n数值为:" << this -> n << endl;
cout << "无符号整数i数值为:" << this -> i << endl;
cout << "字符c数值为:" << this -> c << endl;
cout << "无符号字符u数值为:" << (int)(this -> u) << endl; //以数值形式打印无符号整数
cout << "布尔类型b数值为:" << this -> b << endl;
return;
}
void CTypes::printDeep()
{
cout << "内部成员底层补码0和1信息为:" << endl;
cout << "整数" << this->n << "底层补码0和1信息为:";
this->printBinary(&(this->n), sizeof(this->n));
cout << endl;
cout << "无符号" << this->i << "底层补码0和1信息为:";
this->printBinary(&(this->i), sizeof(this->i));
cout << endl;
cout << "字符" << this->c << "底层补码0和1信息为:";
this->printBinary(&(this->c), sizeof(this->c));
cout << endl;
cout << "无符号字符" << (int)(this->u) << "底层补码0和1信息为:"; //这里同样以数值形式打印无符号整数
this->printBinary(&(this->u), sizeof(this->u));
cout << endl;
cout << "布尔类型" << this->b << "底层补码0和1信息为:";
this->printBinary(&(this->b), sizeof(this->b));
cout << endl;
return;
}
void CTypes::printBinary(void *var, size_t size)
{
unsigned long long now = (1LL << (size*8-1)); // 将 now 设为最高位为 1 ,其余位为0的形式
unsigned long long value;
switch(size) { // 以对应的无符号类型读取 var 指向的值,便于后续位运算处理
case 1:
value = *((unsigned char*)var);
break;
case 2:
value = *((unsigned short*)var);
break;
case 4:
value = *((unsigned long*)var);
break;
case 8:
value = *((unsigned long long*)var);
break;
default:
value = (1LL << 63);
}
int num = 0;
while(now) {
cout << (bool)(now&value);
num ++;
now >>=1; // 通过 now 每次右移自左向右打印底层存储
if(num == 8) // 字节之间以空格隔开
{
cout << ' ';
num = 0;
}
}
return;
}
int main()
{
CTypes t1;
CTypes t2(-10, 10, 'K', 200, 1);
cout << "注意,整数在底层是按照补码存放,正整数的原码 = 反码 = 补码;" << endl;
cout << "负数的反码是原码符号位不变,数值位取反,补码是反码加1。" << endl;
cout << "下面是缺省构造成员底层内部信息:" << endl;
t1.printDeep();
cout << "下面是t2(-10,10,'K',200,1)构造后,成员底层内部信息:" << endl;
t2.printDeep();
cout << endl;
label1:
string input = "";
cout << "请选择操作:" << endl;
cout << "1. 设置类所有内部成员数值,并回显" << endl;
cout << "2. 打印类所有成员内部底层0和1表示信息" << endl;
cout << "3. 退出" << endl;
cout << "请输入选项 (1-3):";
while (input != "3")
{
getline(cin, input);
if (input == "1")
{
t1.setValue();
cout << endl;
cout << "信息回显:" << endl;
t1.printValue();
cout << endl;
goto label1; // 使用 goto 来重新打印默认信息
}
else if (input == "2")
{
t1.printDeep();
cout << endl;
goto label1;
}
else if (input == "3")
{
break;
}
else
{
cout << "请您输入选项 (1-3),为正整数,请重新来!" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
```
### 期末大作业
#### 题目
Move.h
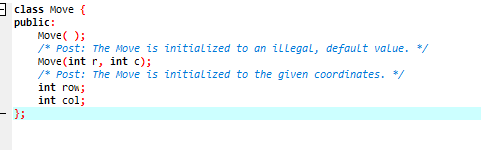
MyStack.h
Board.h

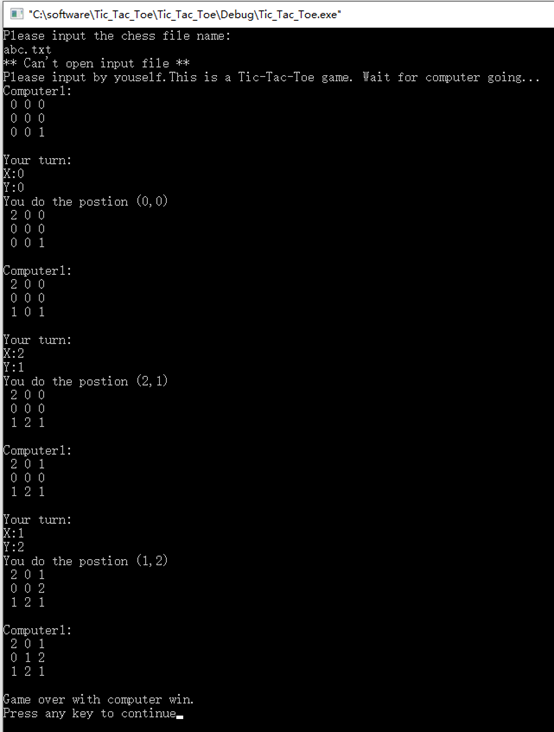
1. 当输入无效棋谱文件名称时,程序要求人自行和电脑对战,运行效果如下图
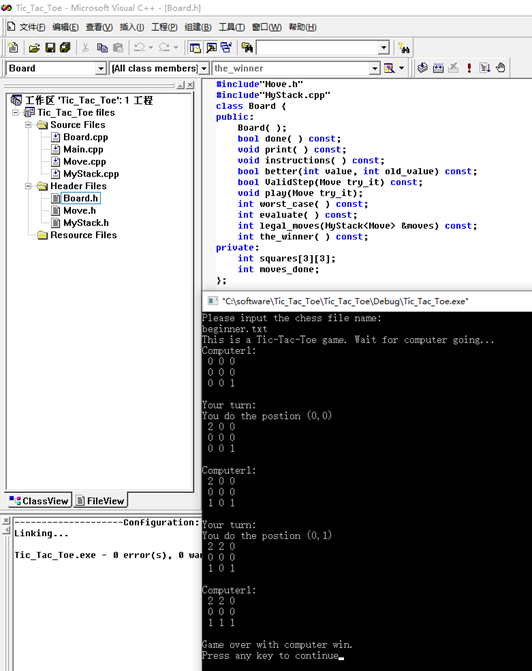
2. 当输入初学者棋谱beginer.txt时,运行效果如下图
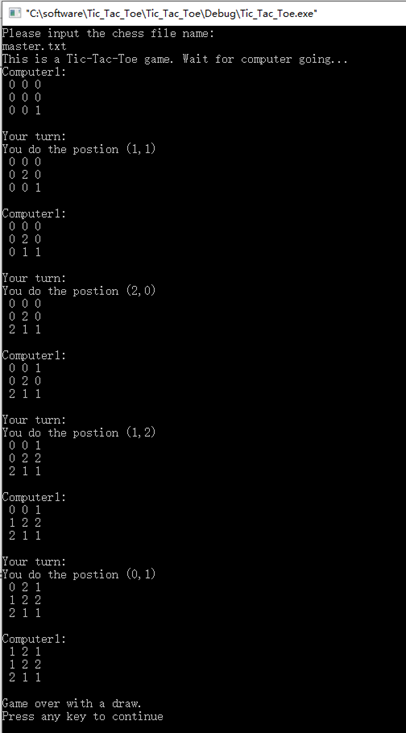
3. 当输入高手棋谱master.txt时,运行效果如下图
```text title="beginner.txt"
0 0
0 1
0 2
1 0
1 1
1 2
2 0
2 1
2 2
```
```text title="master.txt"
1 1
2 0
1 2
0 1
```
#### 参考答案
```cpp title="Move.h"
class Move
{
public:
Move();
Move(int r, int c);
int row;
int col;
};
Move::Move()
{
row = -1;
col = -1;
}
Move::Move(int r, int c)
{
row = r;
col = c;
}
```
```cpp title="MyStack.h"
enum Error_code
{
underflow,
overflow,
success
};
const int maxstack = 10;
template
class MyStack
{
public:
MyStack();
bool empty() const;
Error_code pop();
Error_code top(Stack_entry &item) const;
Error_code push(const Stack_entry &item);
private:
int count;
Stack_entry entry[maxstack];
};
template
MyStack::MyStack()
{
count = 0;
}
template
bool MyStack::empty() const
{
return count <= 0;
}
template
Error_code MyStack::pop()
{
if(empty())
{
return underflow;
}
count--;
return success;
}
template
Error_code MyStack::top(Stack_entry &item) const
{
if(empty())
{
return underflow;
}
item = entry[count - 1];
return success;
}
template
Error_code MyStack::push(const Stack_entry &item)
{
if(count >= maxstack)
{
return overflow;
}
entry[count] = item;
count++;
return success;
}
```
```cpp title="Board.h"
#include
#include "Move.h"
#include "MyStack.h"
class Board
{
public:
Board();
bool done() const;
void print() const;
void instructions() const;
bool better(int value, int old_value) const;
bool ValidStep(Move try_it) const;
void play(Move try_it);
int worst_case() const;
int evaluate() const;
int legal_moves(MyStack &moves) const;
int the_winner() const;
private:
int squares[3][3];
int moves_done;
};
Board::Board()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
squares[i][j] = 0;
moves_done = 0;
}
bool Board::done() const
{
return moves_done == 9 || the_winner() > 0;
}
void Board::print() const
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
std::cout << " " << squares[i][j];
}
std::cout << '\n';
}
std::cout << '\n';
}
void Board::instructions() const
{
std::cout << "This is a Tic-Tac-Toe game. Wait for computer going...\n";
}
bool Board::ValidStep(Move try_it) const
{
return (squares[try_it.row][try_it.col] == 0);
}
void Board::play(Move try_it)
{
squares[try_it.row][try_it.col] = moves_done % 2 + 1;
moves_done++;
}
int Board::the_winner() const
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
if (squares[i][1] != 0 &&
squares[i][1] == squares[i][0] &&
squares[i][1] == squares[i][2])
return squares[i][1];
if (squares[1][i] != 0 &&
squares[1][i] == squares[0][i] &&
squares[1][i] == squares[2][i])
return squares[1][i];
}
if (squares[1][1] != 0)
{
if (squares[1][1] == squares[0][0] &&
squares[1][1] == squares[2][2])
return squares[1][1];
if (squares[1][1] == squares[0][2] &&
squares[1][1] == squares[2][0])
return squares[1][1];
}
return 0;
}
int Board::legal_moves(MyStack &moves) const
{
int count = 0;
while (!moves.empty())
moves.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
if (squares[i][j] == 0)
{
moves.push(Move(i, j));
count++;
}
return count;
}
int Board::evaluate() const
{
int winner = the_winner();
if(winner == 1) return 10-moves_done;
else if(winner == 2) return moves_done-10;
else return 0;
}
bool Board::better(int value, int old_value) const
{
if(moves_done%2) return valueold_value;
}
int Board::worst_case() const
{
if(moves_done%2) return 10;
else return -10;
}
```
```cpp title="main.cpp"
#include "Board.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int look_ahead(const Board &game, int depth, Move &recommended)
{
if (game.done() || depth == 0)
return game.evaluate();
else
{
MyStack moves;
game.legal_moves(moves);
int value, best_value = game.worst_case();
while (!moves.empty())
{
Move try_it, reply;
moves.top(try_it);
Board new_game = game;
new_game.play(try_it);
value = look_ahead(new_game, depth - 1, reply);
if (game.better(value, best_value))
{
best_value = value;
recommended = try_it;
}
moves.pop();
}
return best_value;
}
}
void play(std::vector> rem)
{
Board game;
Move recommended;
int x, y;
int i = 9;
int now = 0;
game.instructions();
while (!game.done())
{
look_ahead(game, i, recommended);
game.play(recommended);
std::cout << "Computer:\n";
game.print();
if (game.done())
break;
std::cout << "Your turn:\n";
if (now < rem.size())
{
x = rem[now].first;
y = rem[now].second;
}
else
{
std::cout << "X:";
std::cin >> x;
std::cout << "Y:";
std::cin >> y;
}
Move me(x, y);
game.play(me);
game.print();
i--;
}
if (game.the_winner() == 1)
std::cout << "Game over with computer win.\n";
else if (game.the_winner() == 2)
std::cout << "Game over with you win.\n";
else
std::cout << "Game over with a draw.\n";
}
std::vector> read(std::string file)
{
freopen(file.c_str(),"r",stdin);
std::string line;
std::vector> rem;
while(std::getline(std::cin,line))
{
if(line.size()==0) break;
std::istringstream record(line);
int x,y;
record >> x >> y;
rem.push_back({x,y});
}
freopen("CON","r",stdin);
return rem;
}
int main()
{
std::string filename;
std::cout << "Please input the chess file name:\n";
std::cin >> filename;
std::ifstream file(filename);
std::vector> rem;
if(file.good())
{
rem = read(filename);
}
else
{
std::cout << "** Can't open input file **\n";
std::cout << "Please input by youself.";
}
play(rem);
return 0;
}
```